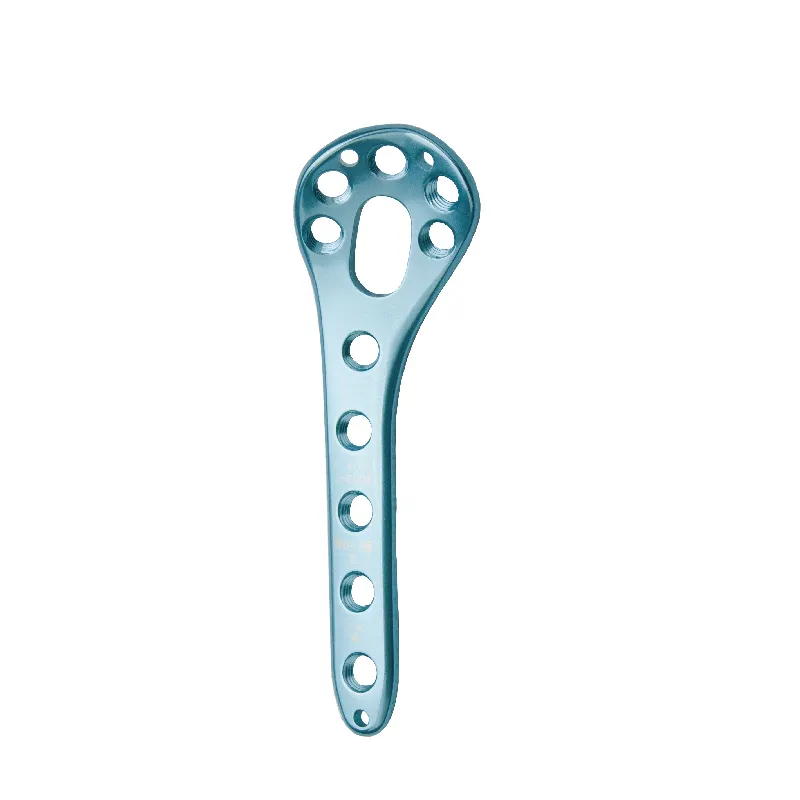
Anatomie clinique fondamentale pour la formation à la vente de plaques fémorales médiales distales
Anatomie fémorale essentielle : condyle médial, jonction métaphyso-épiphyse et repères des tissus mous
Maîtriser l'anatomie fémorale distale est une exigence absolue pour les représentants commerciaux qui accompagnent la mise en œuvre de plaques fémorales médiales distales. Trois repères anatomiques critiques déterminent le succès chirurgical :
- La condyle médial constitue la surface portante principale, nécessitant un modelage précis de la plaque afin d'éviter toute incongruité articulaire
- La jonction métaphyso-épiphyse détermine la trajectoire des vis pour éviter toute atteinte de la plaque de croissance chez les patients jeunes
- Insertions des tissus mous (en particulier les insertions du ligament collatéral médial et du grand adducteur) guident les approches mini-invasives
Des études biomécaniques récentes confirment que l'identification erronée de ces repères anatomiques augmente le risque de mauvaise réduction de 37 % (Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma 2023). Les représentants qui savent décrire précisément les limites vasculaires — comme la proximité de l'artère fémorale à moins de 1,5 cm en médial — acquièrent immédiatement une crédibilité en salle d'opération lors des consultations traumatologiques.
Pourquoi la maîtrise de l'anatomie prévient les malentendus lors des consultations en salle d'opération
Connaître solide la connaissance de l'anatomie change vraiment la manière dont les représentants commerciaux interviennent dans ces situations intenses en salle d'opération. Les chirurgiens utilisent souvent des termes comme « fragment médial de Hoffa » ou demandent une « fixation proximale sans toucher le canal adducteur ». Les commerciaux qui ne maîtrisent pas ces notions spécifiques finissent par provoquer des retards coûteux. Selon une étude publiée l'année dernière dans Clinical Orthopaedics, environ 28 % des erreurs liées aux implants sont dues à des malentendus terminologiques. Et lorsque les représentants ne comprennent pas correctement les concepts relatifs aux tissus mous, cela ajoute en moyenne environ 22 minutes aux interventions de révision d'urgence. Ces chiffres montrent clairement que la compréhension de l'anatomie chirurgicale n'est pas simplement un atout, mais une nécessité pour des opérations efficaces.
En revanche, les représentants maîtrisant les subtilités de la classification AO/OTA — comme distinguer les fractures partielles articulaires 33-A3 des fractures articulaires complètes 33-C3 — deviennent des partenaires stratégiques. Ils anticipent des préoccupations telles que la comminution médiale nécessitant un double plaquage, montrant ainsi comment une compréhension anatomique approfondie influence directement le choix des implants et la séquence chirurgicale.
Maîtrise des techniques chirurgicales grâce à une simulation immersive spécifique aux représentants
Simulation étape par étape de l'application de la plaque : de l'exposition au serrage des vis verrouillables
Les internes en médecine développent une mémoire musculaire grâce à des modules de formation en réalité virtuelle qui simulent des scénarios chirurgicaux réels. Le programme commence par des techniques de base, comme l'accès à l'articulation du genou et la remise en place des os cassés, avant d'aborder la mise en forme de plaques métalliques autour de la courbure de l'os de la jambe inférieure. Au fur et à mesure de leur progression, les stagiaires acquièrent une expérience pratique en plaçant précisément les vis là où elles doivent aller, sans endommager les nerfs et vaisseaux sanguins voisins, et le système fournit un retour immédiat en cas d'erreur. La dernière étape se concentre spécifiquement sur le positionnement exact de ces vis verrouillantes, grâce à une technologie sensible au toucher qui imite ce que ressentent réellement les chirurgiens pendant les opérations. Les médecins ayant suivi ce type de formation immersive retiennent généralement plus rapidement comment gérer les fractures complexes de type 33-C que ne le permettent les méthodes traditionnelles, beaucoup affirmant pouvoir se remémorer les procédures environ 40 % plus vite lorsqu'ils discutent de cas avec des chirurgiens seniors.
Intégration au laboratoire de cadavres : Renforcer la crédibilité et la confiance dans les situations traumatologiques à haut risque
Travailler dans des laboratoires de cadavres comble l'écart entre la théorie enseignée en classe et le développement pratique des compétences. Les professionnels de santé manipulent directement des tissus humains réels lorsqu'ils s'entraînent à placer des plaques exactement aux endroits complexes où la métaphyse rejoint l'épiphyse. Ils ressentent également directement comment les différents os réagissent sous pression lors de l'insertion de vis, une expérience que les manuels scolaires ne peuvent tout simplement pas transmettre. L'exposition à la gestion des pertes sanguines et à la manipulation de tissus mous délicats renforce considérablement la crédibilité en salle d'opération. La majorité des stagiaires déclarent se sentir nettement plus confiants après ces séances, particulièrement lorsqu'ils doivent gérer des fractures complexes impliquant plusieurs fragments osseux. Et soyons honnêtes, rien ne prépare mieux aux situations d'urgence que des répétitions réalistes qui réduisent les hésitations maladroites et les malentendus survenant en milieu chirurgical sous haute pression.
Indications, classification des fractures et logique de sélection des implants
AO/OTA 33-A3 et 33-C1—C3 : Association des schémas de fracture à l'adaptation de la plaque distale médiale du fémur
Le système de classification de l'AO Foundation/Association des Traumatismes Orthopédiques aide à déterminer la bonne approche pour la fixation des fractures. Lorsqu'il s'agit de fractures de type 33-A3 présentant des motifs transversaux ou obliques extra-articulaires, les chirurgiens ont souvent recours à la plaque distale médiale du fémur. Cette plaque fonctionne bien car elle enjambe la zone métaphysaire sans toucher directement la surface articulaire. Les choses deviennent toutefois plus complexes avec les fractures de type 33-C1 à C3. Ces cas présentent des surfaces articulaires de plus en plus complexes, rendant ainsi particulièrement importants les vis verrouillantes et la forme anatomique de certaines plaques. Les caractéristiques de verrouillage multidirectionnel aident à maintenir un bon alignement dans ces zones fracturées et préviennent l'affaissement en varus, une complication fréquemment observée chez les patients souffrant d'ostéoporose, selon des études récentes telles que le rapport de Ponemon de 2023.
Les représentants commerciaux se familiarisent avec les fractures de type 33-C, qui représentent environ 60 % de toutes les lésions du fémur distal. Celles-ci constituent les principales raisons de recommander notre produit, car il permet à la fois la réparation de la surface articulaire et assure un bon soutien dans la région du diaphyse osseuse. Lors des séances de formation, nous insistons sur le fait que les schémas de fracture 33-A3 simples peuvent souvent être traités avec des vis classiques, tandis que les cas complexes de type 33-C3 nécessitent absolument des systèmes verrouillables spéciaux. Lorsque les représentants comprennent ces distinctions, ils peuvent mieux adapter les implants aux patients individuels en fonction d'éléments tels que la résistance osseuse et l'âge du patient. Cette connaissance permet d'éviter les confusions pendant les interventions chirurgicales et fait de nos collaborateurs des interlocuteurs précieux lorsque les chirurgiens choisissent une option thérapeutique dans les blocs opératoires à travers tout le pays.
Formation commerciale Plaque fémorale distale médiale : Différenciation, messages clés et mise en œuvre sur le terrain
Une formation efficace à la vente permet aux commerciaux de transformer leur expertise technique en succès commercial en mettant l'accent sur la différenciation propre à chaque plaque :
- Mettre en avant les avantages de conception tels que les profils plats et les configurations de vis de verrouillage qui réduisent l'irritation des tissus mous
- Démontrer la supériorité biomécanique à l'aide de données sur la stabilité en torsion et de références en matière de résistance à la fatigue
- Insister sur les avantages centrés sur le chirurgien, notamment une instrumentation simplifiée et une adaptabilité intraopératoire
Le message doit passer de caractéristiques génériques à des résultats cliniques. Les commerciaux doivent expliquer comment la géométrie de la plaque améliore la stabilité dans les fractures complexes, préciser la compatibilité avec les approches chirurgicales courantes et citer des preuves montrant une réduction de 19 % des réinterventions pour les fractures intra-articulaires.
La mise en œuvre sur le terrain repose sur une maîtrise contextuelle. La simulation prépare les commerciaux à des situations critiques :
- Répondre aux objections budgétaires en calculant les économies à long terme grâce à un nombre moindre de complications
- Naviguer entre les préférences des chirurgiens grâce à des évaluations de compatibilité procédurale
- Résoudre les conflits liés au choix des implants en utilisant la logique de classification AO/OTA
Une étude de vente de technologie médicale de 2023 a révélé que les représentants disposant d'une formation spécifique aux dispositifs ont obtenu des taux d'adoption par les chirurgiens supérieurs de 27 % en contextualisant la valeur pendant les consultations traumatologiques. La maîtrise de l'anatomie, de la technique et de la communication transforme la connaissance technique en confiance — la monnaie essentielle dans les ventes orthopédiques.
FAQ
Quels sont les repères anatomiques clés pour une intervention chirurgicale avec plaque du fémur distal ?
Les repères anatomiques clés pour une intervention chirurgicale avec plaque du fémur distal incluent le condyle médial, la jonction métaphyso-épiphyseaire et les insertions essentielles des tissus mous comme le ligament collatéral médial et le grand adducteur.
En quoi la maîtrise de l'anatomie profite-t-elle aux représentants commerciaux lors des consultations en salle d'opération ?
La maîtrise de l'anatomie permet aux représentants commerciaux de comprendre et d'utiliser efficacement les termes chirurgicaux, d'éviter des malentendus coûteux et d'améliorer leur crédibilité ainsi que leur efficacité en salle d'opération.
Quels sont certains avantages de la formation par simulation pour les techniques chirurgicales ?
La formation par simulation pour les techniques chirurgicales aide les résidents médicaux à développer une mémoire musculaire, améliore leur rapidité et leur précision lors de la réalisation de procédures et fournit un retour immédiat pour un meilleur apprentissage.
En quoi le système de classification AO/OTA aide-t-il au traitement des fractures ?
Le système de classification AO/OTA guide les chirurgiens dans le choix de la méthode de fixation appropriée en classant les fractures selon des schémas spécifiques, ce qui facilite le choix efficace des implants et la planification chirurgicale.
Pourquoi une formation commerciale efficace est-elle importante pour la vente de plaques du fémur médial distal ?
Une formation à la vente efficace permet aux représentants de communiquer des connaissances techniques, de différencier les caractéristiques des produits et de répondre aux préoccupations des chirurgiens, ce qui entraîne des taux d'adoption plus élevés et un succès commercial accru.
Table of Contents
- Anatomie clinique fondamentale pour la formation à la vente de plaques fémorales médiales distales
- Maîtrise des techniques chirurgicales grâce à une simulation immersive spécifique aux représentants
- Indications, classification des fractures et logique de sélection des implants
- Formation commerciale Plaque fémorale distale médiale : Différenciation, messages clés et mise en œuvre sur le terrain
-
FAQ
- Quels sont les repères anatomiques clés pour une intervention chirurgicale avec plaque du fémur distal ?
- En quoi la maîtrise de l'anatomie profite-t-elle aux représentants commerciaux lors des consultations en salle d'opération ?
- Quels sont certains avantages de la formation par simulation pour les techniques chirurgicales ?
- En quoi le système de classification AO/OTA aide-t-il au traitement des fractures ?
- Pourquoi une formation commerciale efficace est-elle importante pour la vente de plaques du fémur médial distal ?
 EN
EN
 FR
FR
 ES
ES
 AR
AR